Blade coating adds a protective layer to knives, helping stainless steels last longer and resist rust. This coating also boosts safety by reducing friction and making cleaning easier.
For knife sellers, choosing the right blade coating is critical—it directly impacts product durability, customer satisfaction, and the overall value of your offerings. Dive into the essentials of selecting blade coatings and find the optimal solutions that best serve your customers.
What Is A Blade Coating
A blade coating is a thin layer of material added to a knife or tool blade. This layer can be metal, ceramic, or polymer based. Its main purpose is to protect the blade and improve how it performs.
Notably, this coating doesn’t compromise the inherent properties of the steel. The right coating can extend a blade’s lifespan to thousands of cycles in industrial environments or simplify cleaning in everyday kitchen use.
The application method of the coating also matters—whether sprayed, baked, or chemically bonded, the result is a robust barrier that blocks moisture and slows rust formation.
For properly coated blades, maintenance routines may differ. Always consult your supplier for guidance on care to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Benefits Of Blade Coating
Blade coatings make your knives stronger, protect them from rust, help them cut cleaner, and let you choose from many styles. Coatings do more than just change how a blade looks—they greatly improve how a knife performs and lasts.
- Enhanced Durability & Wear Resistance
Coated blades are significantly more resistant to scratches and wear, lasting up to five times longer than uncoated ones. This durability reduces the frequency of replacements and sharpening.
- Corrosion Protection
Coatings create a barrier against moisture, salts, and chemicals, greatly enhancing corrosion resistance. This keeps blades rust-free, even in humid conditions or when cutting acidic foods.
- Improved Cutting Performance
Coated blades maintain sharper edges longer, preventing rolling and chipping. This results in cleaner cuts and less frequent sharpening, saving time for users.
- Reduced Friction & Sticking
Coatings can lower surface friction by 30-50%, allowing blades to glide smoothly through materials. This reduces sticking, making cleanup easier and speeding up work in high-volume settings.
- Aesthetic Customization
Blade coatings come in various colors and finishes, enabling customers to choose styles that match their preferences or brand image. Unique designs can enhance product appeal and create collectible opportunities.
Buy Wholesale Knives and Start Scaling up with Us Today
Contact us and connect with a sales rep to get a free quote.
Different Types Of Blade Coatings
Blade coatings can boost durability, performance, and resistance to wear or corrosion. Each coating method uses unique materials and processes to match the needs of different knives and cutting tools.
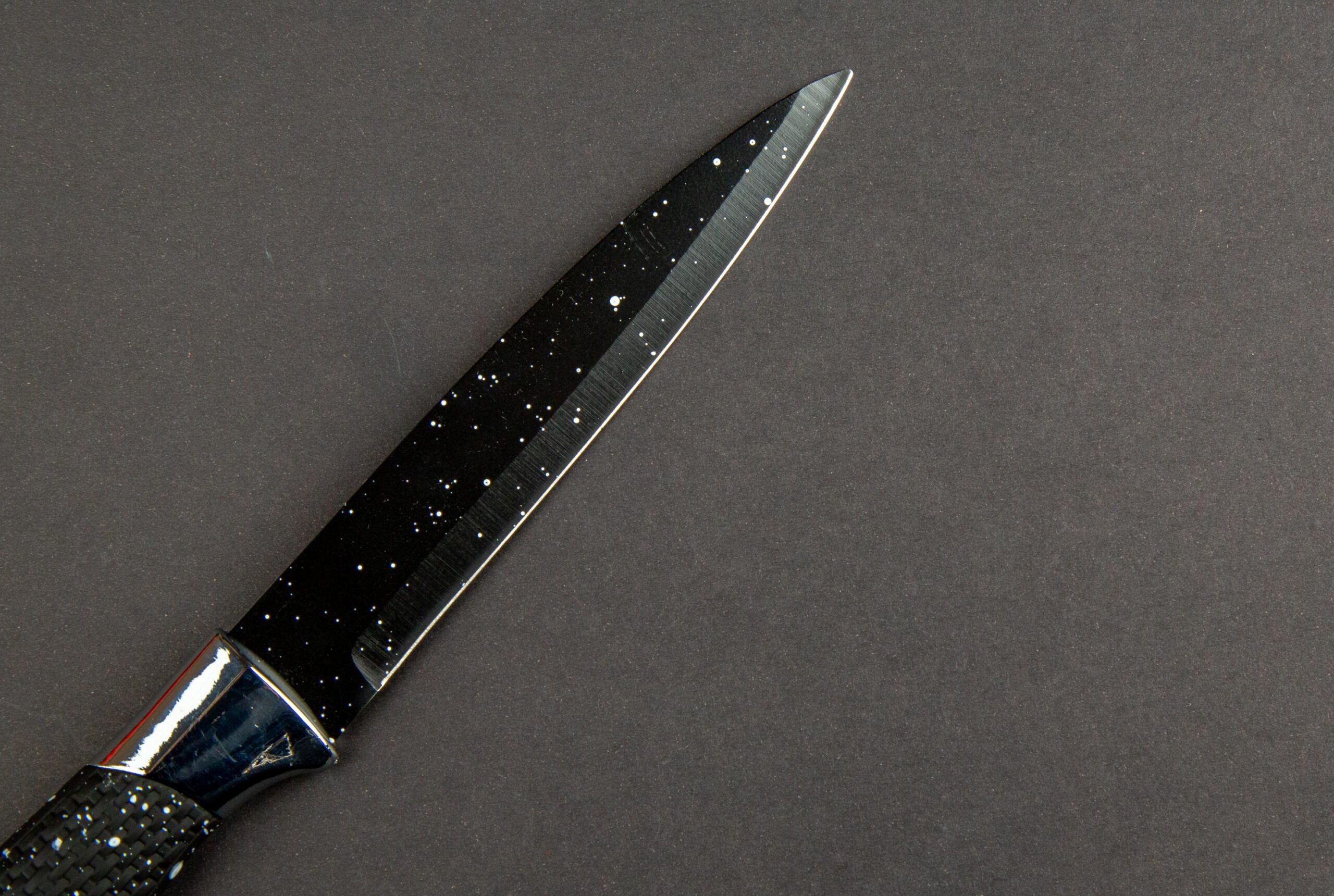

Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) Coatings
PVD coatings use a high-tech vacuum process to deposit thin metal layers onto a blade. Common types include titanium nitride (TiN), titanium carbonitride (TiCN), and diamond-like carbon (DLC).
Uses: Common in both industrial and consumer markets, including cutting tools and surgical instruments.
Pros:
- Hard and scratch-resistant.
- Very thin (a few micrometers), preserving blade shape.
- Low friction surface for easier cutting.
- Chemical resistance, preventing rust and stains.
- Environmentally friendly process.
Cons:
- Higher cost compared to traditional coatings.
- Requires specialized equipment for application.
Titanium Nitride (TiN)
Titanium nitride (TiNi) is one of the most popular metallic coatings for high-performance blades. It is applied using PVD and creates a golden, glossy surface.
Uses: Widely used in professional and industrial blades, especially in food processing and manufacturing.
Pros:
- Increases surface hardness up to 80 Rockwell C.
- Reduces friction, keeping edges sharp longer.
- Strong corrosion resistance in wet environments.
Cons:
- Can be more expensive than other coatings.
- Limited to specific applications where high-performance is required.
Ceramic Coatings

Composed mainly of ceramics, this coating is not as hard as PVD or CVD, but it provides amazing corrosion resistance and heat resistance. They can also add an aesthetic touch with a range of color options. Ceramic coatings enhance the durability of blades in harsh environments.
Uses: Widely used in firearms, knives, and industrial applications.
Pros:
- Excellent corrosion resistance and thermal stability.
- Available in a wide range of colors and finishes.
Cons:
- Can chip or scratch under extreme use.
- Requires precise application for optimal performance.
Teflon/Non-Stick Coatings
Teflon, also known as PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene), is commonly used for non-stick coatings. This is the same material used in non-stick cooking pans.
A Teflon coating on a blade helps prevent food, tape, or sticky materials from clinging to the blade. Teflon also reduces friction, which makes each cut smoother and faster.
Uses: Many utility knives, kitchen knives, and industrial blades use Teflon black nonstick coatings.
Pros:
- Easy to clean and maintain.
- Reduces friction for smoother cutting.
Cons:
Not suitable for high-temperature applications.
Less durable than metal coatings, can wear off over time.
Buy Wholesale Knives and Start Scaling up with Us Today
Contact us and connect with a sales rep to get a free quote.
Powder Coatings
Powder coating involves spraying a dry powder onto the blade, then baking it to form a protective shell. This process creates a thicker coating than PVD or CVD.
Powder-coated blades are popular for their toughness. These coatings resist scratches, chips, moisture, and chemicals, which helps prevent rust. The finish is not as smooth as metal coatings, so it may cause extra drag when cutting.
Uses: Popular in outdoor, camping, and tactical knives.
Pros:
- Tough and resistant to scratches, chips, and moisture.
- Available in many colors with a matte finish.
Cons:
- Thicker than metal coatings, which may increase drag.
- Can chip under rough use.
Paint
Some low-cost blades use paint for a colorful finish. Paint is sprayed or brushed onto the blade and air-dried or baked.
Uses: Common in display knives, kids’ knives, or decorative blades.
Pros:
- Offers a wide range of colors.
- Protects against minor rust.
Cons:
- Least durable; scratches and fades quickly.
- Not suitable for frequent use.
Maintenance & Longevity
- Cleaning
Clean coated blades with mild soap and water, using a soft cloth to avoid damage. Always dry them immediately and avoid abrasive materials that can wear down the coating. Regular cleaning prevents residue buildup and extends the life of the blades.
- Handling
Handle blades carefully to prevent chipping or flaking. Use tools or gloves to minimize direct pressure, and clearly label blades to remind users of their care needs. Transport blades with protective coverings to avoid impact and temperature fluctuations.
- Storage
Store coated blades in a dry environment to prevent corrosion. Use blade racks to keep them separated and ensure proper airflow. For high-value blades, consider airtight containers, and regularly check for moisture to maintain optimal conditions.
Conclusion
Blade coating can make a big difference for your knives. It adds protection against wear, corrosion, and even scratches. Many sellers look for coated blades because they last longer and stay sharp in different conditions.
Choosing the right coating depends on your target market and the type of knives you sell. For example, some coatings are best for outdoor knives, while others fit kitchen tools. Each coating type has its own benefits, like better stealth or durability.
If you buy or sell blades, you should focus on what your buyers want most—function, appearance, and price. Wholesale buyers, retailers, or those building a private label can benefit from reliable suppliers.
Ready to source high-quality coated blades or customize your own? You can request a free quote for your next knife order and take the next step for your business.
Frequently Asked Questions
What should be considered when choosing a blade coating machine for my needs?
First, look at the size and type of products you work with most. Some machines are built for large rolls, while others work better with small sheets or pieces. Match the coater’s max width and speed to your production targets.
Consider the type of coatings you plan to use. Different coatings (such as water-based, solvent-based, or special polymers) may need different settings or even machine parts. Also, think about maintenance and technical support, because downtime can cut into your profits.
Can you explain the main differences between blade coating and other coating methods?
Blade coating spreads material evenly across a surface using a flat blade. This gives you a thin, uniform film, which makes it popular for paper, films, and some textiles.
Compared to roll or spray coating, blade coating gives better control over thickness but may require a smoother substrate. Other methods like spray coating work better for uneven surfaces.